Switzerland is fertile ground for financial innovation as it’s rooted in its strong foundation of overall innovation. Ranked first in the Global Innovation Index for 14 consecutive years (Global Innovation Index, 2023), the country fosters competition and entrepreneurship through a liberal economic framework and business freedom. A culture of openness, supported by a stable legal environment, encourages trust and long-term creativity.
Furthermore, Switzerland boasts a robust financial infrastructure, attracting skilled talent and housing established banks. This, combined with a well-developed educational system including world-class universities specializing in finance, creates a perfect ecosystem for financial innovation to flourish.
On the one hand, it is not surprising that Switzerland boasts an above average density of traditional financial institutions, a fact which is particularly interesting for FinTechs with a B2B business model looking to collaborate with traditional players. A result of this density of financial institutions and the stable and favourable environment, Swiss financial institutions are currently managing USD 2.6 trillion in wealth, more than any other country (Global Wealth Report, 2024). On the other hand, Switzerland is equally attractive for B2C-focused FinTechs due to it’s high proportion of affluent population.
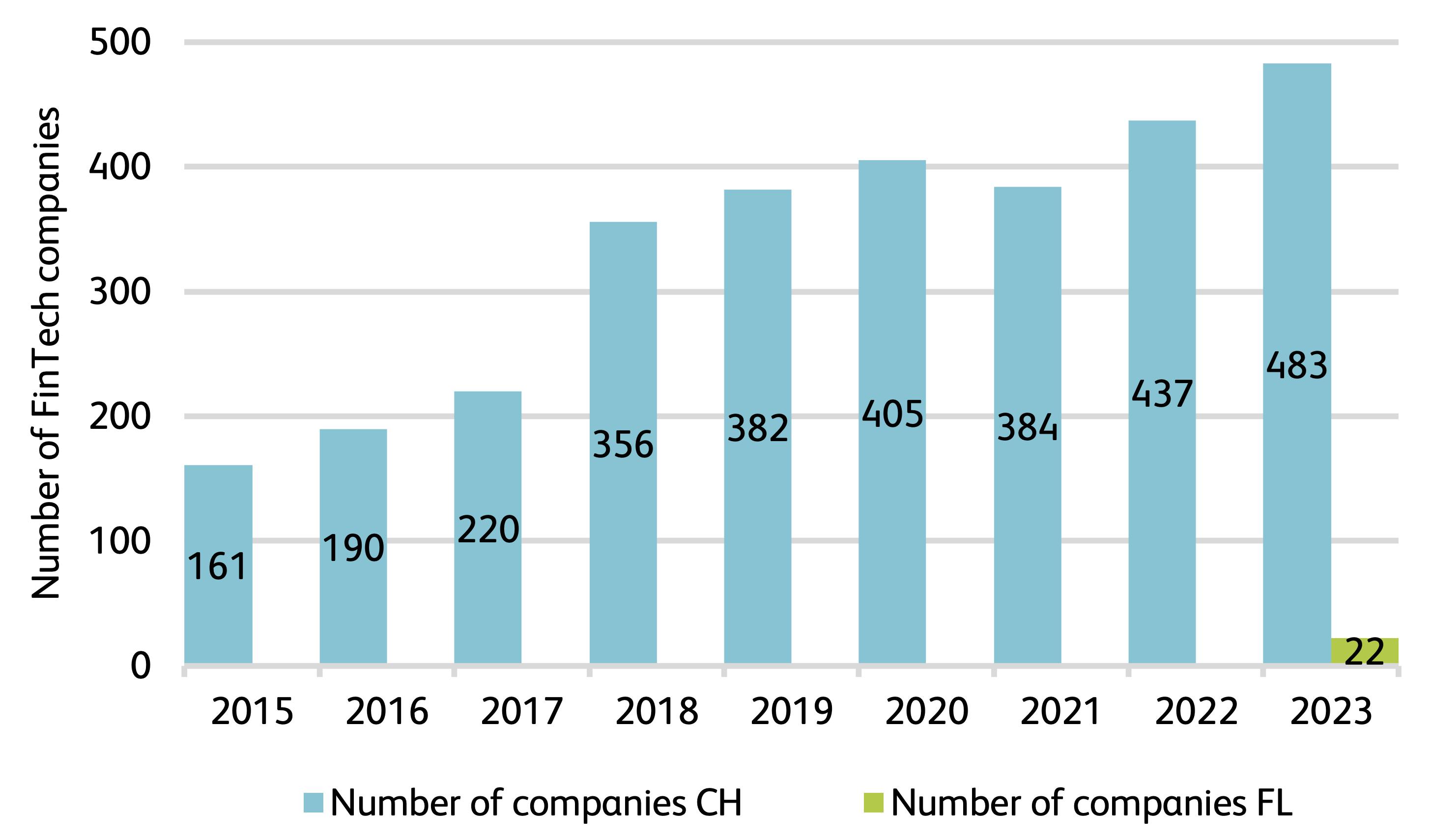
Number of FinTech companies in Switzerland
Source:https://hub.hslu.ch/retailbanking/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2024/03/IFZ_FinTech_Study_2024.pdf
1. Switzerland’s FinTech Strategy
The Federal Department of Finance (FDF), as directed by the Federal Council, issued the Digital Finance report to evaluate and enhance Switzerland’s position in the rapidly evolving digital finance sector. The report outlines strategies for promoting innovation, ensuring regulatory clarity, and addressing challenges such as digital payment systems and FinTech developments, all aimed at strengthening Switzerland's competitiveness in global finance.
These twelve areas not only outline the key actions for strengthening Switzerland's digital finance ecosystem but also reveal significant opportunities for FinTech companies. By aligning with these strategic directions – such as fostering open finance, advancing AI and DLT technologies, and expanding green fintech initiatives – innovative firms can find fertile ground for growth, contribute to the country’s financial transformation, and shape the future of the Swiss financial sector.
1.1. Examine the Legal and Supervisory Framework with Regard to New Configurations and Players
New financial products and service providers are emerging, requiring a review and possible adjustments to Switzerland’s legal and supervisory frameworks.
1.2. Promote and Expand Open Finance
Standardized interfaces can drive innovation in the financial sector by enabling greater participation from all market players.
4.3. Enable the Use of RegTech and SupTech
Innovative technologies in financial regulation and supervision offer efficiency gains but require careful management of associated risks.
4.4. Closely Monitor Developments in Cloud Computing
With financial institutions increasingly using cloud services, legal and regulatory questions must be addressed to ensure compliance.
4.5. Continue Cooperation on Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is essential for the secure functioning of the digital economy, protecting against risks such as cyberattacks while enabling data usage.
4.6. Promote Data Use in the Financial Sector
While there is room for improvement in data-based business models, secure data management is needed to unlock new opportunities.
4.7. Foster Shared Data Use in the Financial Centre
Shared data usage can improve financial operations, combat illicit activities, and optimize services, but requires coordinated efforts across sectors.
4.8. Support the Use of Artificial Intelligence in the Financial Sector
AI can enhance personalization and risk management but concerns regarding data origin and traceability must be addressed.
4.9. Ensure Free Cross-Border Data Flows
Free data movement is vital for global financial activities but must align with Swiss data protection and financial laws.
4.10. Enable Innovative and Responsible Use of DLT in the Financial Sector
Optimizing the regulatory framework for Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is key to harnessing its potential while ensuring secure implementation.
4.11. Continue Efforts to Make Switzerland a Leading Green FinTech Hub
Green fintech is critical to sustainable investing and combating climate change, requiring active promotion both domestically and internationally.
4.12. Strengthen the Innovation Potential of the Financial Sector with an Innovation Platform
FIND has been established to foster fintech innovation, which helps helps the country to position itself as a leading financial hub.
5. Licenses for FinTechs in Switzerland
In Switzerland, while there is no specific license exclusively for FinTech companies, the country offers a range of licenses that cover various business models within the financial sector. These include licenses for portfolio managers, asset managers, broker-dealers, and banks, among others. Additionally, Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs) play an important role in overseeing their members on behalf of the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA), and they themselves are directly supervised by FINMA to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Under the principle of "same risk, same rules," FinTech companies are required to obtain the appropriate license based on their specific business model and activities. For example, a FinTech providing payment services may need a different license than one managing investment portfolios or offering brokerage services. This framework ensures that the regulatory environment remains consistent and proportionate to the risks posed by each business model, supporting both innovation and financial stability in Switzerland's dynamic FinTech landscape.
For more information, please consult the website of FINMA on licenses and SRO information. These resources provide detailed guidance on licensing and regulatory frameworks in Switzerland's financial sector.